01-webpack 打包原理
Webpack 打包原理
本文适合于有一点点的 webpack 的基础,和 js 模块的基础的人群
1. 示例代码的项目结构
// 创建目录 安装依赖
mkdir 01-base
npm init -y
npm i webpack webpack-cli
mkdir src
Src新建文件结构如下
// src/index.js
const str = require("./a");
console.log("hello" + str);
// src/a.js
module.exports = "aaa";
// webpack.config.js [webpack 默认读取的配置]
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/index.js",
mode: "development",
};
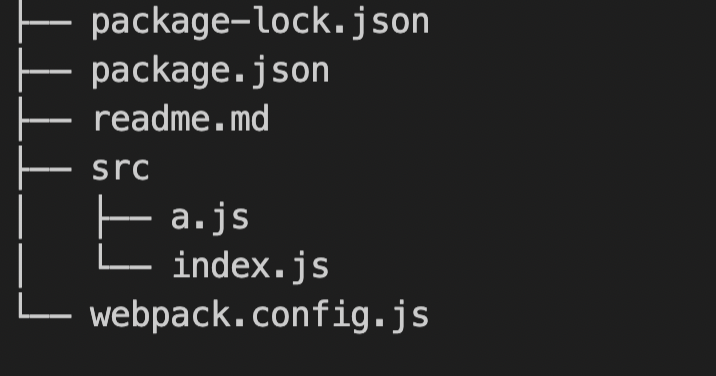
2.打包结果在 dist 目录
main.js 经过删除注释以后的代码如下
/*
*注意:已经使用了“eval”devtool(默认情况下可能是在“开发”模式下)。
*此devtool既不用于生产,也不用于可读的输出文件。
*它使用“eval()”调用在浏览器devtools中创建单独的源文件。
*如果试图读取输出文件,请选择其他devtool(https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/)
*或者使用“devtool:false”禁用默认devtool。
*如果要查找生产就绪输出文件,请参阅模式:“生产”(https://webpack.js.org/configuration/mode/).
*/
(() => {
// webpackBootstrap
var __webpack_modules__ = {
"./src/a.js": (module) => {
eval(
"module.exports = 'aaa'\n\n//## sourceURL=webpack://01-base/./src/a.js?"
);
},
"./src/index.js": (
__unused_webpack_module,
__unused_webpack_exports,
__webpack_require__
) => {
eval(
"const str = __webpack_require__(/*! ./a */ \"./src/a.js\")\nconsole.log('hello' + str);\n\n//## sourceURL=webpack://01-base/./src/index.js?"
);
},
};
// The module cache
var __webpack_module_cache__ = {};
// The require function
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// Check if module is in cache
var cachedModule = __webpack_module_cache__[moduleId];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
return cachedModule.exports;
}
// Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
var module = (__webpack_module_cache__[moduleId] = {
// no module.id needed
// no module.loaded needed
exports: {},
});
// Execute the module function
__webpack_modules__[moduleId](module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
// Return the exports of the module
return module.exports;
}
// startup
// Load entry module and return exports
// This entry module can't be inlined because the eval devtool is used.
var __webpack_exports__ = __webpack_require__("./src/index.js");
})();
a.整体分析 匿名函数自执行
- 避免了变量的污染详见文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/CurryLi/p/11652540.html
b.函数代码入口处在最下方
// startup
// Load entry module and return exports
// This entry module can't be inlined because the eval devtool is used.
var __webpack_exports__ = __webpack_require__("./src/index.js");
c.’webpack_require 分析
// The module cache
var __webpack_module_cache__ = {};
// The require function 见名知意 模拟的 require 函数
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// moduleId 取值为 ./src/index.js
// Check if module is in cache 理论是 Memoization 空间换时间
var cachedModule = __webpack_module_cache__[moduleId];
if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
// 找到模块的缓存 返回该模块 缓存的 exports 属性
return cachedModule.exports;
}
// 之前没有加载过 该模块
// Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
var module = (__webpack_module_cache__[moduleId] = {
// no module.id needed
// no module.loaded needed
exports: {},
});
// Execute the module function 读取变量 __webpack_modules__ 里的 ./src/index 【见下一个分析 d 位置 】
__webpack_modules__[moduleId](module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
// 解析__webpack_modules__[moduleId] 的值是一个函数 (module, module.exports, __webpack_require__) 是函数的参数
// Return the exports of the module
return module.exports;
}
d.变量 webpack_modules:存储文件和代码的信息
将依赖 进行数据化对象存储 方便读取 各模块的代码信息
var __webpack_modules__ = {
"./src/a.js": (module) => {
eval("module.exports = 'aaa'");
},
"./src/index.js": (
__unused_webpack_module,
__unused_webpack_exports,
__webpack_require__
) => {
eval(
"const str = __webpack_require__(\"./src/a.js\")\nconsole.log('hello' + str);"
);
},
};
e:最后可以通过 node js 的调试功能 来断点查看 webpack 的运行原理
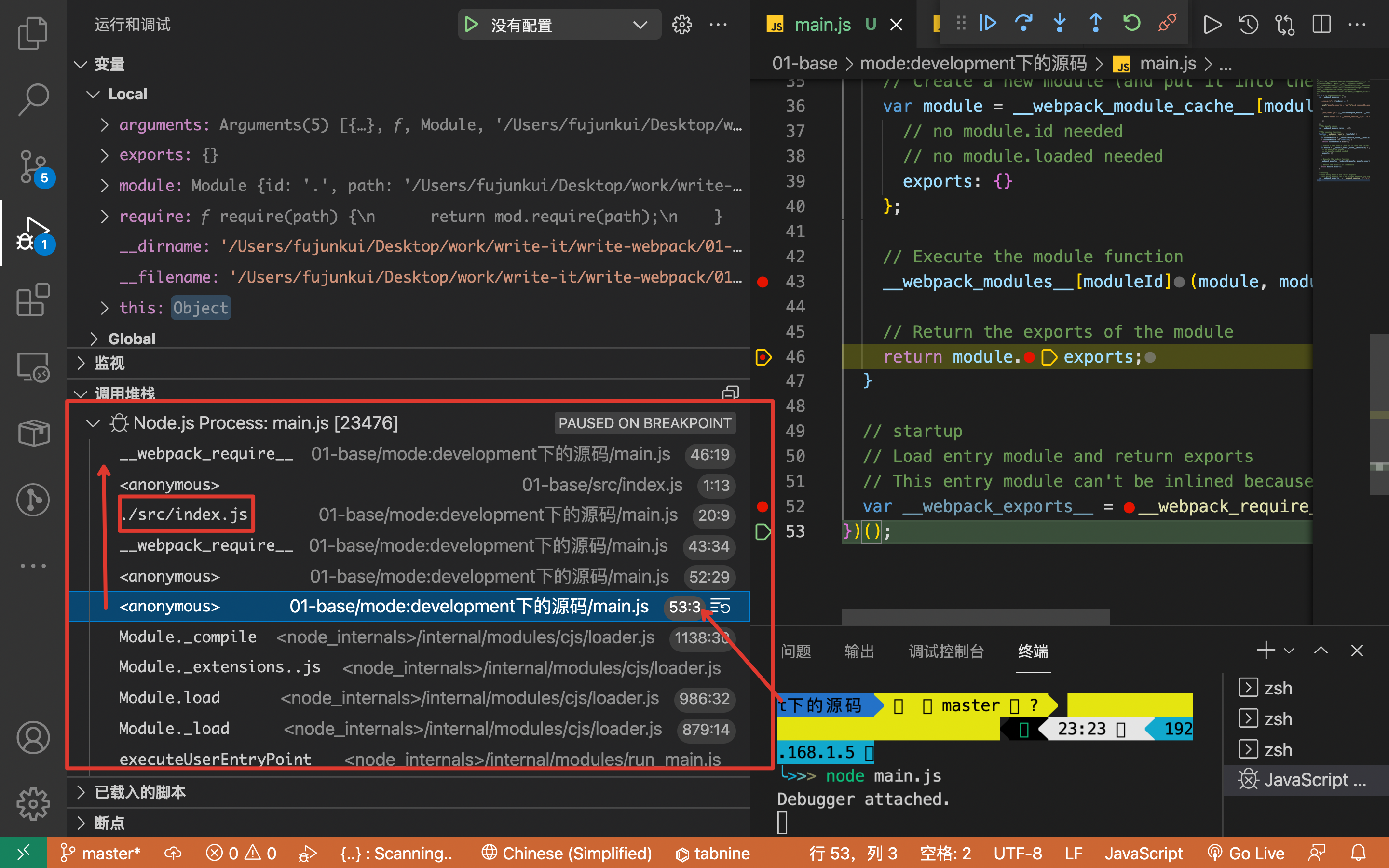
3.关键词
- webpack
- eval 函数
- 模块和代码的存储关系
- 使用缓存 Memoization
- 递归调用