Babel 插件的编写(上)
学习的背景
- es6 是如何转换为 es5 的?
- 为啥 之前 jsx 需要 手动导入 react ,现在不需要了?
- 国际化内容 需要写 t 函数的 地方太多 ,懒得写了。(业务方面)
1. babel 常用包的介绍 (写插件必备知识)
代码 转 语法树的 官网:https://astexplorer.net/
1. Babylon 是 Babel 的解析器,代码转为 AST 语法树
npm init -y进行项目的初始化 搭建- Babylon 是 Babel 的解析器,是 将 代码 转换为 AST 语法树的 工具,现在来安装它
npm install --save babylon - 新增
babylon-demo.mjs(注意是 mjs 结尾的,方便使用 ESmodule 语法),写入 如下内容。调用 babylon.parse生成 ast 语法树
import * as babylon from "babylon";
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
console.log(ast);
// Node {
// type: "File",
// start: 0,
// end: 38,
// loc: SourceLocation {...},
// program: Node {...},
// comments: [],
// tokens: [...]
// }
2. Babel-traverse 来操作 AST 语法树
npm install --save babel-traverse安装 依赖。- 利用 语法树 将 code 中的 n 替换为 x。(别急 下一步 就是 根据新的 语法树 生成代码)
import * as babylon from "babylon";
import traverse from "babel-traverse";
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
// 对 抽象语法树 一层层的 遍历
traverse.default(ast, {
// 树 的节点 会 作为 参数 传入 enter 函数
enter(path) {
// 如果当前节点 是 Identifier 并且 name 是 n。就替换为 x
if (path.node.type === "Identifier" && path.node.name === "n") {
path.node.name = "x";
}
},
});
3. babel-generator根据修改的语法树 生成代码 和源码映射(source map)
- 安装 依赖
npm install --save babel-generator - 将 AST 语法树 生成代码
import * as babylon from "babylon";
import traverse from "babel-traverse";
import generate from "babel-generator";
// 原始代码
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
// ast 是对象 属于引用型
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
// 对 抽象语法树 一层层的 遍历
traverse.default(ast, {
// 树 的节点 会 作为 参数 传入 enter 函数
enter(path) {
// 如果当前节点 是 Identifier 并且 name 是 n。就替换为 x
// 因为 ast 是对象,所以 此处做的变更会 直接影响到 ast
if (path.node.type === "Identifier" && path.node.name === "n") {
path.node.name = "x";
}
},
});
// 对节点操作过以后的代码
const targetCode = generate.default(ast).code;
console.log("targetCode", targetCode);
// targetCode function square(x) {
// return x * x;
// }
4. 发现对节点的判断 需要写的代码很多,抽离出公共的包来进行节点的判断。babel-types(AST 节点里的 Lodash 式工具库)
- 安装:
npm install --save babel-types - 优化上面代码的 AST 节点的 if 判断。
import * as babylon from "babylon";
import traverse from "babel-traverse";
import generate from "babel-generator";
// 注意 node_modules 模块里 导出的是 default
import { default as t } from "babel-types";
// 原始代码
const code = `function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
// ast 是对象 属于引用型
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
// 对 抽象语法树 一层层的 遍历
traverse.default(ast, {
// 树 的节点 会 作为 参数 传入 enter 函数
enter(path) {
// 如果当前节点 是 Identifier 并且 name 是 n。就替换为 x
// 因为 ast 是对象,所以 此处做的变更会 直接影响到 ast
// if (
// path.node.type === "Identifier" &&
// path.node.name === "n"
// ) {
// path.node.name = "x";
// }
if (t.isIdentifier(path.node, { name: "n" })) {
path.node.name = "x";
}
},
});
// 对节点操作过以后的代码
const targetCode = generate.default(ast).code;
console.log("targetCode", targetCode);
// targetCode function square(x) {
// return x * x;
// }
5. 通过 AST 来生成 CODE 可读性 太差。使用babel-template来实现占位符的来生成代码。
- 安装依赖:
npm install --save babel-template - 当前的需求是:我不想手动导入 文件 a 依赖。即:const a = require("a");这句话 我不想写。
- 首先构建 ast 的模板:判断哪些是变量,哪些是 语法。
// 构建模板
const buildRequire = template(`
const IMPORT_NAME = require(SOURCE);
`);
- 使用 变量 进行 填充
// 创建ast
const astImport = buildRequire({
IMPORT_NAME: t.identifier("a"),
SOURCE: t.stringLiteral("a"),
});
- 分析 何时塞入 这段 ast 。使用 https://astexplorer.net/ 分析 得知。代码和 图片如下
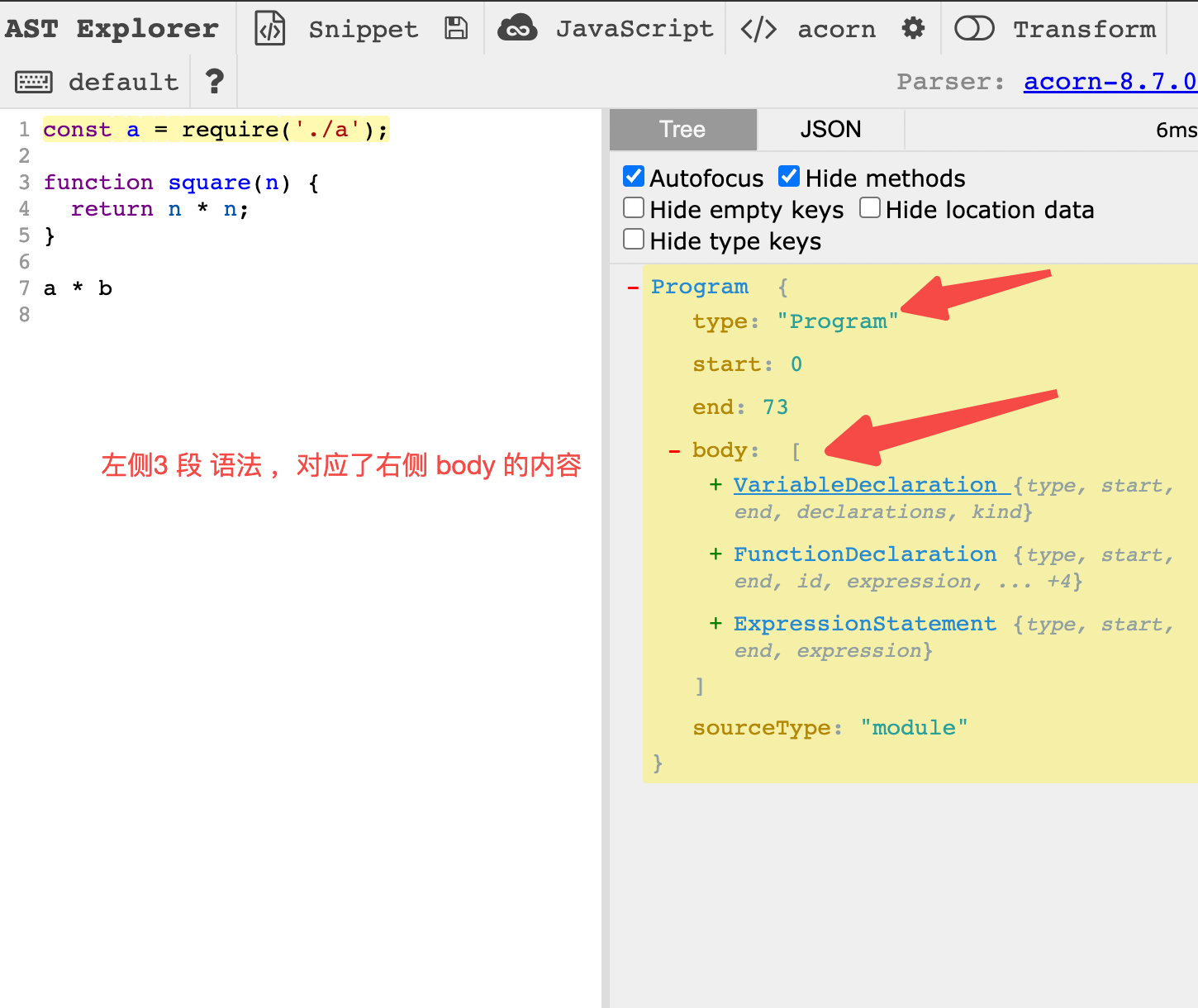
import * as babylon from "babylon";
import traverse from "babel-traverse";
import generate from "babel-generator";
import { default as template } from "babel-template";
// 注意 node_modules 模块里 导出的是 default
import { default as t } from "babel-types";
// 构建模板
const buildRequire = template(`
const IMPORT_NAME = require(SOURCE);
`);
// 创建ast
const astImport = buildRequire({
IMPORT_NAME: t.identifier("a"),
SOURCE: t.stringLiteral("a"),
});
// 原始代码
const code = `
function square(n) {
return n * n;
}`;
// ast 是对象 属于引用型
const ast = babylon.parse(code);
// 对 抽象语法树 一层层的 遍历
traverse.default(ast, {
// 树 的节点 会 作为 参数 传入 enter 函数
enter(path) {
// 如果当前节点 是 Identifier 并且 name 是 n。就替换为 x
// 因为 ast 是对象,所以 此处做的变更会 直接影响到 ast
// if (
// path.node.type === "Identifier" &&
// path.node.name === "n"
// ) {
// path.node.name = "x";
// }
if (t.isIdentifier(path.node, { name: "n" })) {
path.node.name = "x";
}
// 在程序的开头 塞进去 我的 ast
if (t.isProgram(path.node)) {
console.log("塞入我写的 ast");
path.node.body.unshift(astImport);
}
},
});
// 对节点操作过以后的代码
const targetCode = generate.default(ast).code;
console.log("targetCode", targetCode);
// 塞入我写的 ast
// targetCode const a = require("a");
// function square(x) {
// return x * x;
// }
2. 开始 撸 Babel 的插件
1. 开始撸插件代码 之前 必须要有一个 方便调试的 babel 的环境
- 安装 babel 核心包 @babel/core (文档:https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/usage#%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83%E5%BA%93)。`npm install --save-dev @babel/core`
- 新建 demo 代码
index.js
// index.js
let bad = true;
const square = (n) => n * n;
新建插件
plugin2.js// plugin.js
module.exports = function ({ types: babelTypes }) {
return {
name: "deadly-simple-plugin-example",
visitor: {
Identifier(path, state) {
if (path.node.name === "bad") {
path.node.name = "good";
}
},
},
};
};- 新建
core-demo.js使用 babel-core 来编译 代码
const babel = require("@babel/core");
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
// 导入 index.js 的代码 并使用 插件 plugin2 转换
babel
.transformFileAsync("./index.js", {
plugins: [path.join(__dirname, "./plugin2.js")],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.code);
// 转换后的代码 写入 dist.js 文件
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(__dirname, "./dist.js"), res.code, {
encoding: "utf8",
});
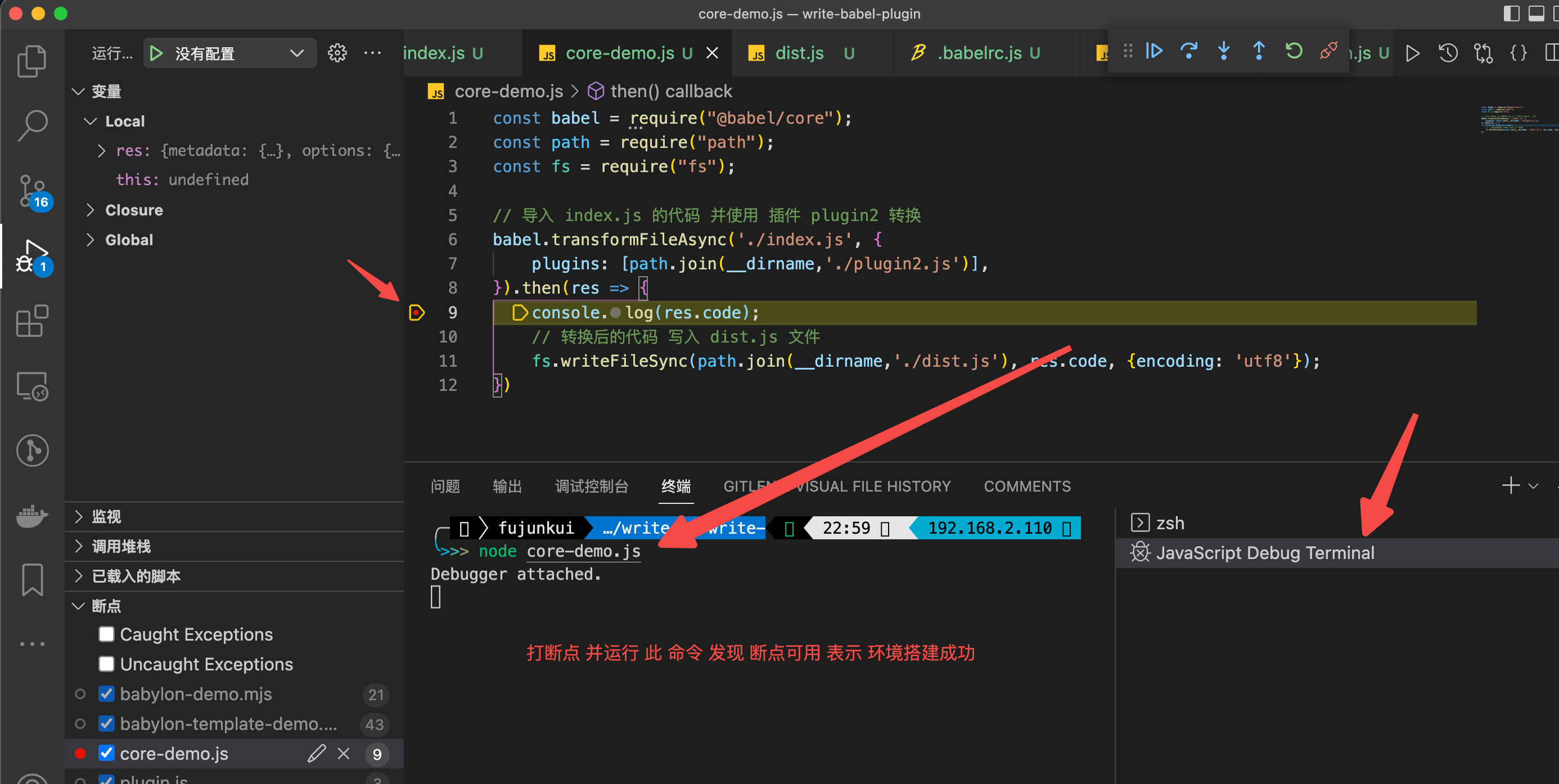
});- 测试 断点是否生效(方便后期调试)
vscode 中 新建 debug 终端
- 新建
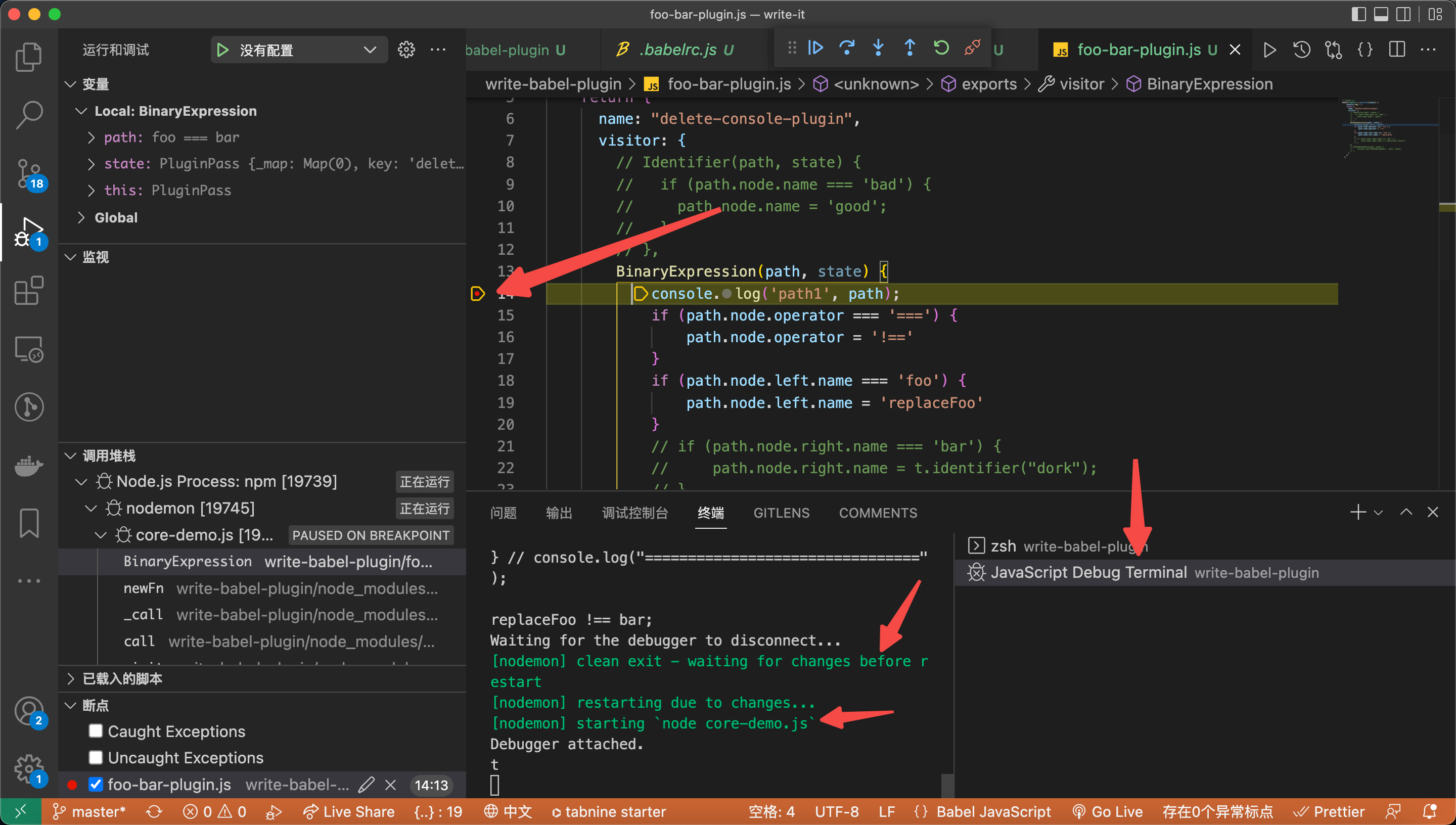
2. 使用 nodemon 包优化环境,提高调试的效率 (nodemon + debug 提高效率)
- 安装依赖:
npm i nodemon - 配置 package.json 的 script 命令为:(监听文件变更时候忽略 dist.js ,因为 dist 的变更会引起 脚本的重新执行,脚本的重新执行又 产生新的 dist.js)
"babylon": "nodemon core-demo.js --ignore dist.js"
- 开启 debug 终端,运行
npm run babylon即可看到文件变更 会自动走到断点里
babel 插件需要写的东西太多,本小节只是完成环境的搭建。具体请见下节。