Babel 插件的编写(下)
本文并未详细介绍所有的 babel path 节点的相关 api,详细的 关于 path 节点的相关文档 请见 官方推荐文档(中文 有点老旧) 或者 根据官方原版 英文文档 翻译的 中文文档(已经向 官方 提了 PR 但是暂未合并),推荐的 是 先看 此文档,发现其中 部分 api 不熟悉 的时候 再去查 api 文档,印象深刻。
1. babel 插件的 API 规范
- Babel 插件 本质上是一个函数,该函数 接受 babel 作为参数,通过 会 使用
babel参数里的types函数
export default function(babel) {
// plugin contents
}
// or
export default function({types}) {
// plugin contents
}
- 返回的 是一个 对象。对象的
visitor属性是这个插件的主要访问者。visitor的 每个函数中 都会接受 2 个 参数:path和state
export default function ({ types: t }) {
return {
visitor: {
// 此处的函数 名 是从 ast 里 取的
Identifier(path, state) {},
ASTNodeTypeHere(path, state) {},
},
};
}
2. 来个 demo 实现 ast 层面的 代码替换
目的: 将 foo === bar; 转为 replaceFoo !== myBar;
- 首先 通过 https://astexplorer.net/ 来分析 ast 结构。
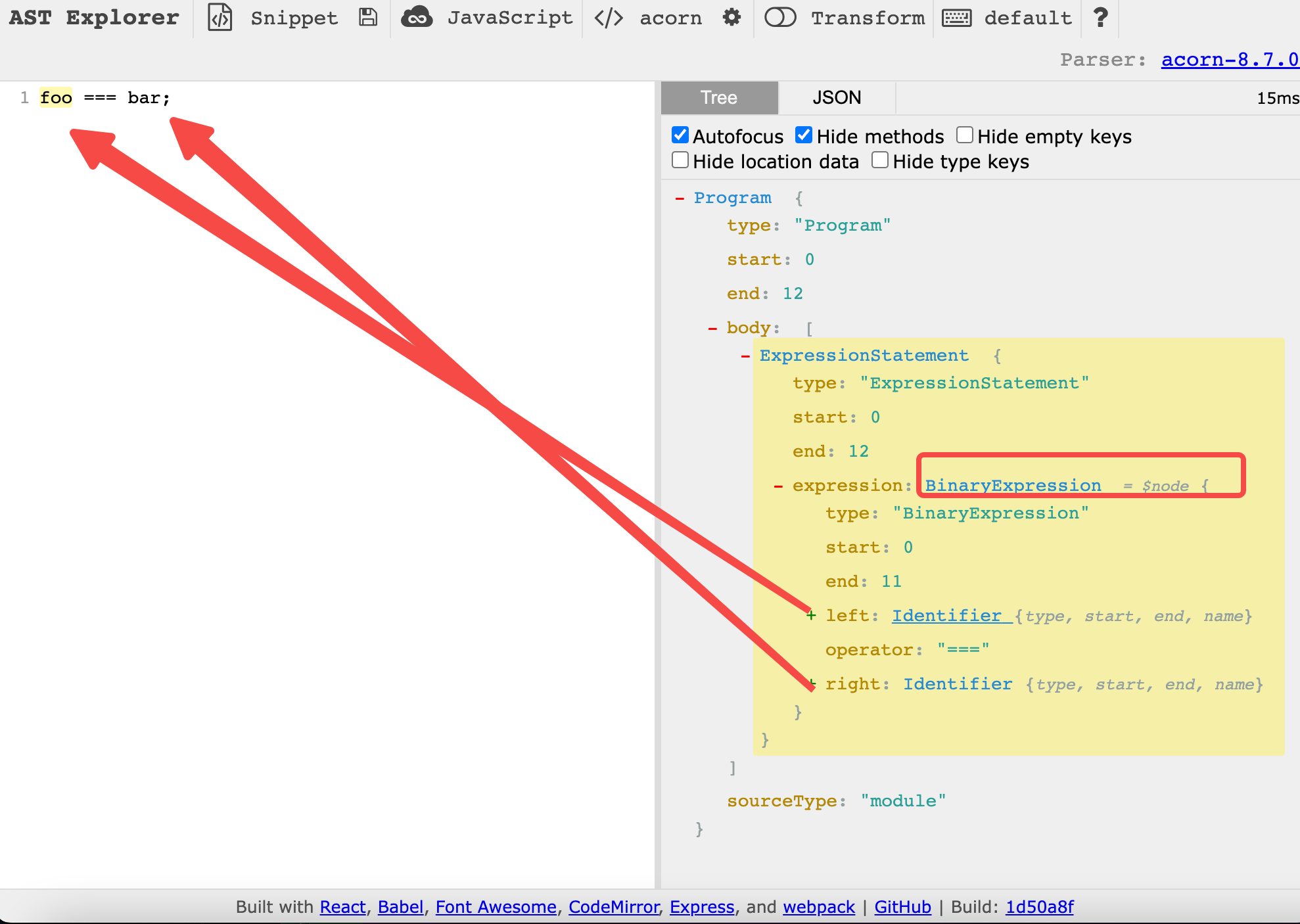
{
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"operator": "===",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "foo"
},
"right": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "bar"
}
}
- 从
BinaryExpression添加 访问者 进行 ast 节点处理,可以 看到 当operator为 === 的时候 需要进行处理。代码如下
// plugin.js
module.exports = function ({ types }) {
console.log("t");
return {
visitor: {
BinaryExpression(path, state) {
console.log("path1", path);
// 不是 !== 语法的 直接返回
if (path.node.operator !== "===") {
return;
}
},
},
};
};
进行 ast 节点的 更改,因为 ast 是一个对象,可以 对 path 字段 直接更改其属性值即可。 比如 将 left 和 right 节点 的 name 进行修改。
// plugin.js
module.exports = function ({ types }) {
console.log("t");
return {
visitor: {
BinaryExpression(path, state) {
console.log("path1", path);
if (path.node.operator !== "===") {
return;
}
if (path.node.operator === "===") {
path.node.operator = "!==";
}
if (path.node.left.name === "foo") {
path.node.left.name = "replaceFoo";
}
if (path.node.right.name === "bar") {
path.node.right.name = "myBar";
}
},
},
};
};从 index.js 经过 上述 babel 插件处理以后得出 dist.js 内容为:
// index.js
foo === bar;
a = 123;
// babel 插件处理后
replaceFoo !== myBar;
a = 123;
3. 上一小节 掌握了 ast 节点 基础的 修改 和 访问,加深一下 ast 节点的操作
1. 获取 ast 节点的 属性值:path.node.property
BinaryExpression(path) {
path.node.left;
path.node.right;
path.node.operator;
}
2. 获取 该属性 内部的 path (节点信息): path.get(xxx)
BinaryExpression(path) {
path.get('left'); // 返回的是一个 path 性的
}
Program(path) {
path.get('body.0');
}
3. 检查节点的类型, 通过 babel 参数自带的 types 函数进行检查。
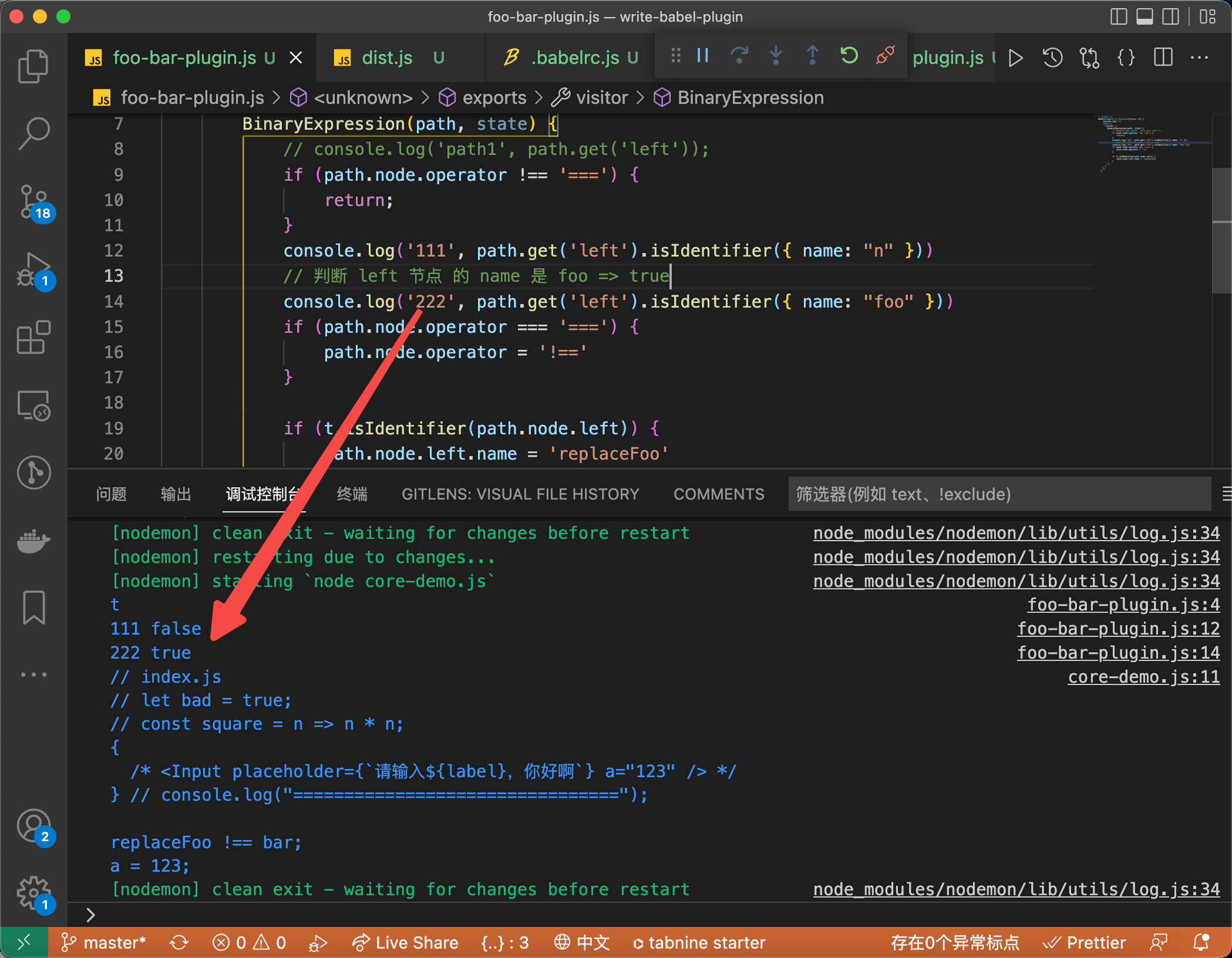
- 简单判断节点的类型
// plugin.js
module.exports = function ({ types: t }) {
console.log("t");
return {
visitor: {
BinaryExpression(path, state) {
console.log("path1", path.get("left"));
if (path.node.operator !== "===") {
return;
}
if (path.node.operator === "===") {
path.node.operator = "!==";
}
// 等同于 path.node.left.type === "Identifier"
if (t.isIdentifier(path.node.left)) {
path.node.left.name = "replaceFoo";
}
},
},
};
};
- 判断节点的类型,外加 浅层属性的校验
BinaryExpression(path) {
if (t.isIdentifier(path.node.left, { name: "n" })) {
// ...
}
}
功能上等同于:
BinaryExpression(path) {
if (
path.node.left != null &&
path.node.left.type === "Identifier" &&
path.node.left.name === "n"
) {
// ...
}
}
4. 再来一道关于 ast 操作节点的题小试身手(关键还是学会看 ast 语法树和 尝试一些 ast 节点相关的 api)
当前程序代码为:
function square(n) {
return n * n;
}
const a = 2;
console.log(square(a));
目标程序代码是:
function newSquare(n, left) {
return left ** n;
}
const a = 2;
console.log(newSquare(a, 222));
整体操作 ast 语法树的分析逻辑:(结尾会放完整代码)
- 将
square函数命名 进行 更名,改为newSquare - 将
newSquare(因为square参数 节点的 ast 名称 已经改为了newSquare)的入参增加 一个left参数 - 将
n * n进行 替换,换成left ** n; - 在调用
square处 进行修改,首先将函数名 改为newSquare,然后在,对该函数的入参增加 一个222
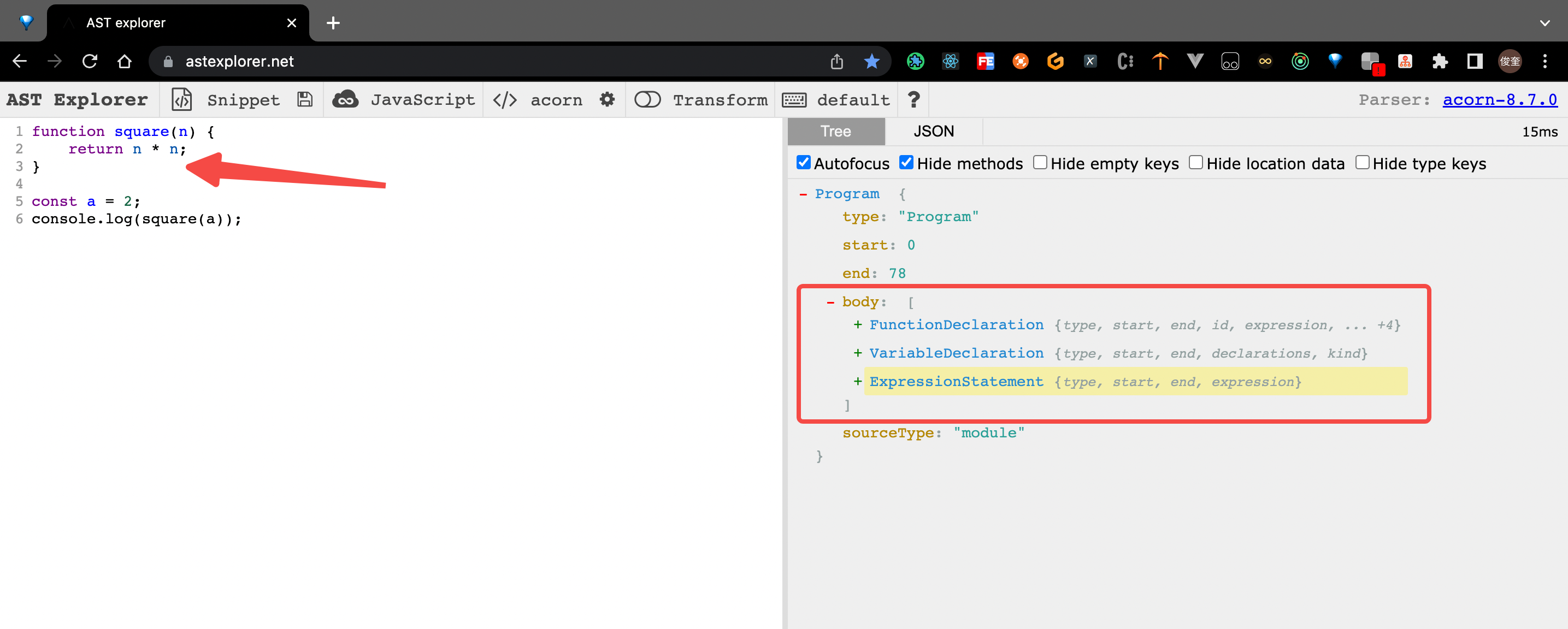
1. 首先分析 原代码的 ast 语法树
可以看到当前程序 代码 被解析为 3 段 ast 语法树 节点
2. 接下来分析 函数定义 的这个节点
鼠标滑选 1-3 行,发现右侧 自动展开了。
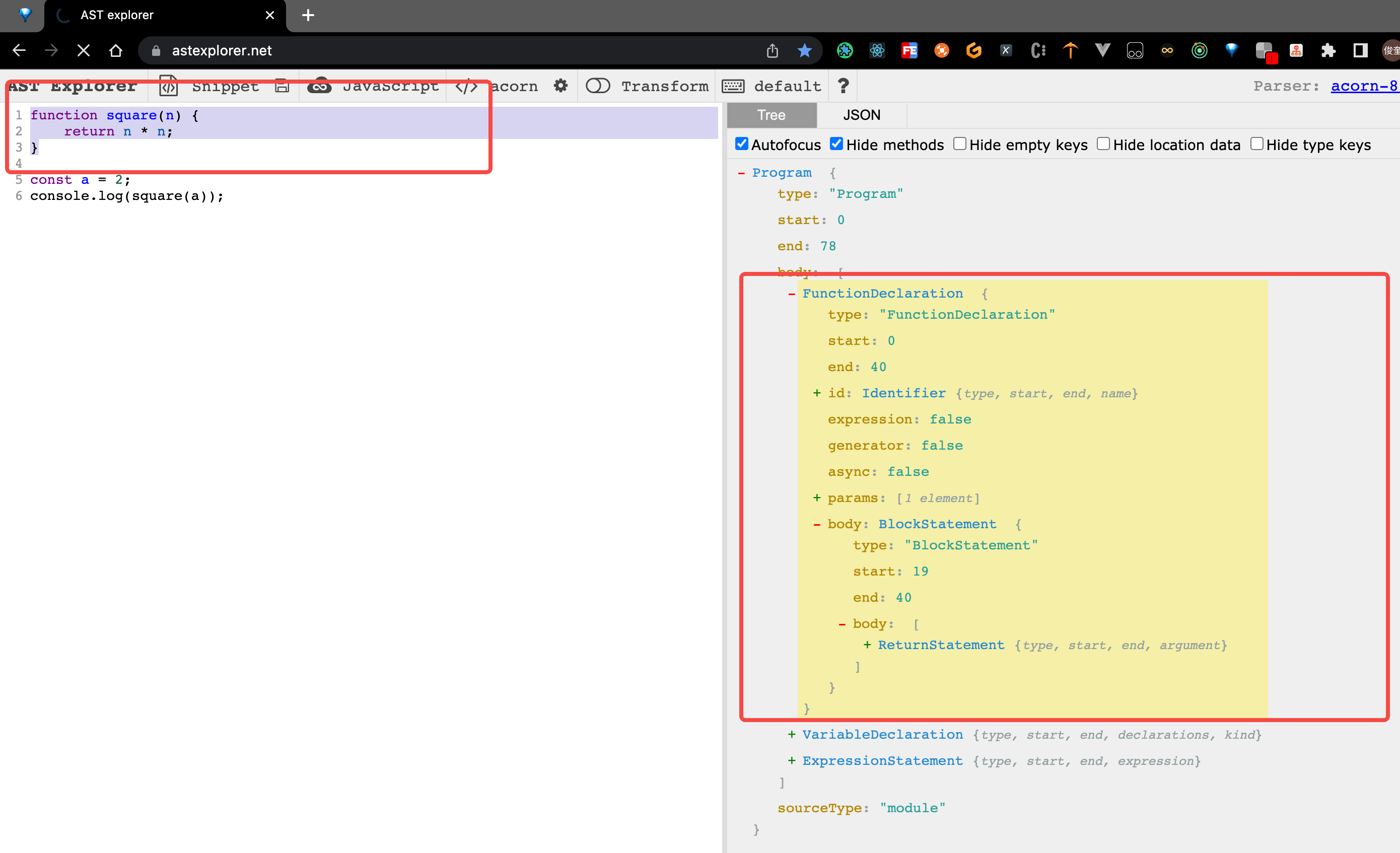
3. 进行第一步:将 square函数命名 进行 更名,改为 newSquare
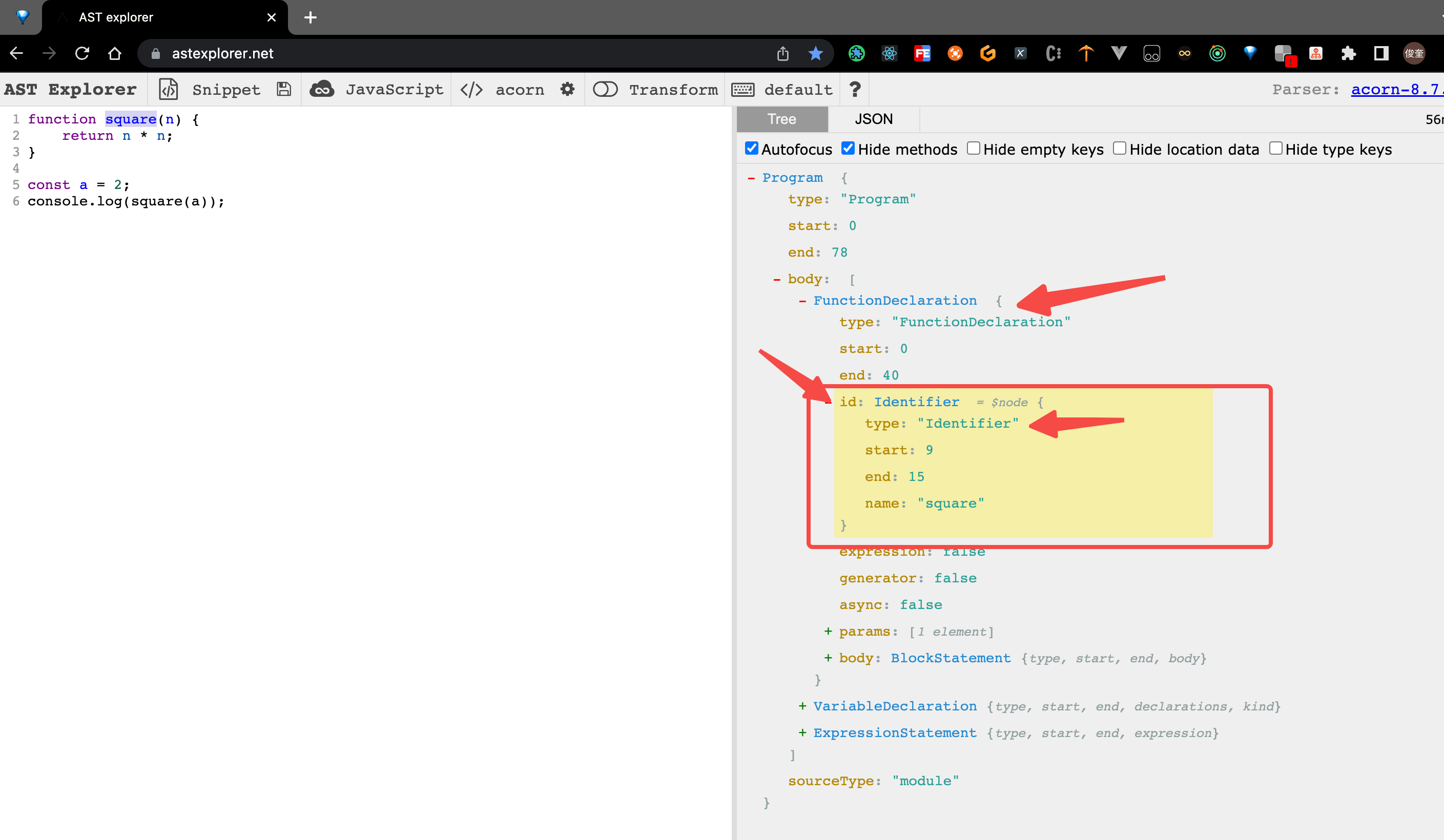
由图看出,如何确定 当前的节点是 square 函数的命名 节点呢?(1 分钟 思考一下)。
- 节点的类型首先是:Identifier 类型,并且 当前节点 的
name字段是 square - 节点的 父级 节点的 类型 是 FunctionDeclaration 的。
伪代码如下:
// 新建 变量,记录 新函数的函数名
const newName = "newSquare";
// 获取当前 函数的 父级。查找最接近的父函数或程序:
const parentFunc = path.getFunctionParent();
if (parentFunc) {
// 当前父节点 是 square函数 并且当前的节点的key是 id(此处是为了确认 square 的函数命名节点)。
// 然后对此函数进行重命名 从 square 改为 newName
if (parentFunc.node.id.name === "square" && path.key === "id") {
console.log("对 square 进行重命名:", newName);
path.node.name = newName;
}
}
4. 接下来 将 newSquare的入参增加 一个 left参数。
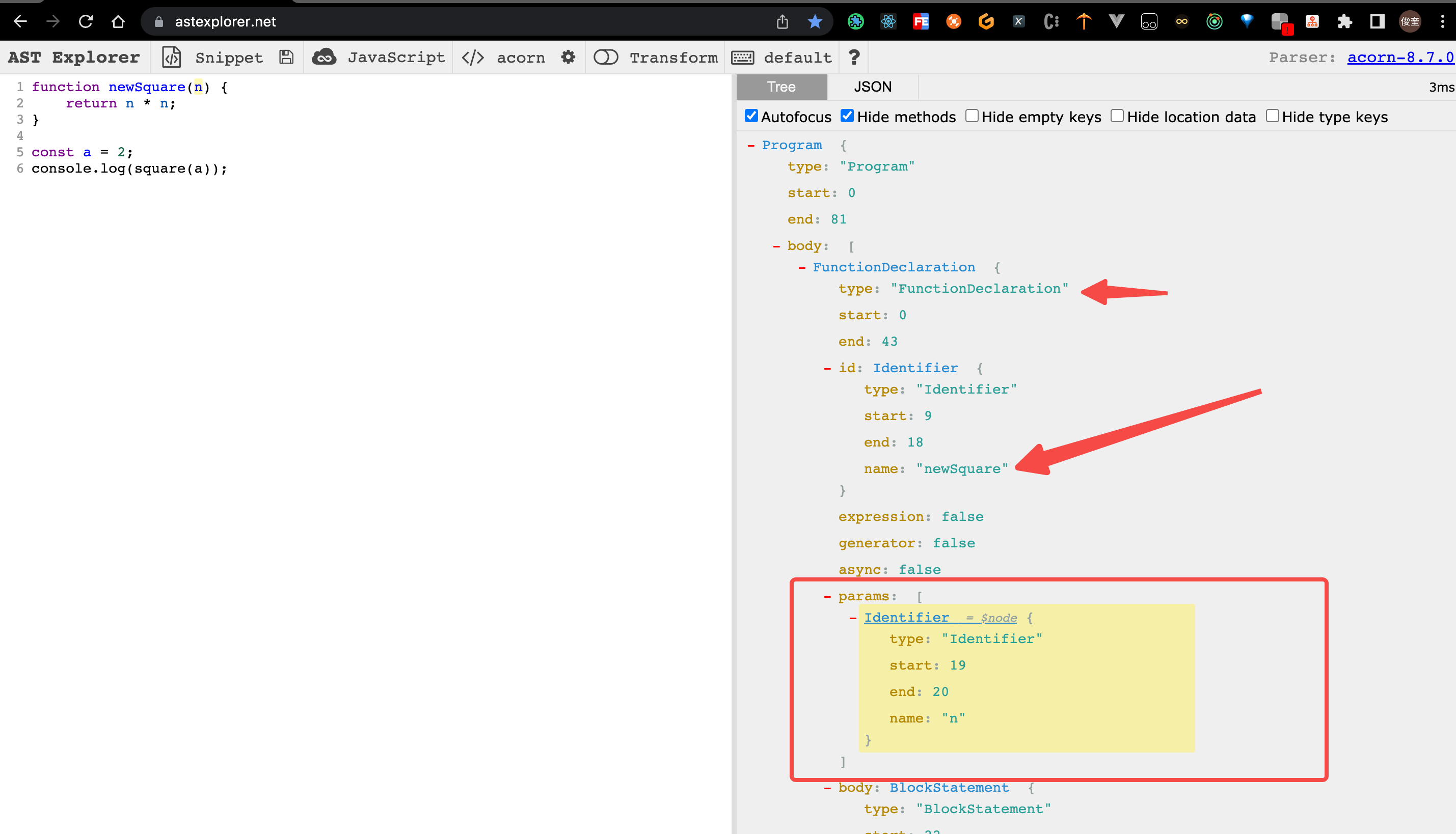
- 当前节点 的 类型 是
Identifier类型,并且是 在 名为params的 列表里 (列表,就意味着 可以 进行 增删改查了) - 当前节点的 父级 节点类型 是 FunctionDeclaration 的,并且 父级节点下的 id 的 name 属性 已经变更为了
newSquare
伪代码如下:
// 当前父节点 是 square函数 并且当前的节点的listKey是 params(此处是为了排除 square 的函数命名节点)。
// 此处是在重命名后才会走的 逻辑 所以 该节点 父级的 名称判断用的是 newName 而不是 square
if (
parentFunc.type === "FunctionDeclaration" &&
parentFunc.node.id.name === newName &&
path.listKey === "params"
) {
console.log("新增函数参数 left");
path.container.push(t.identifier("left"));
}
5. 将 n * n 进行 替换,换成 left ** n;
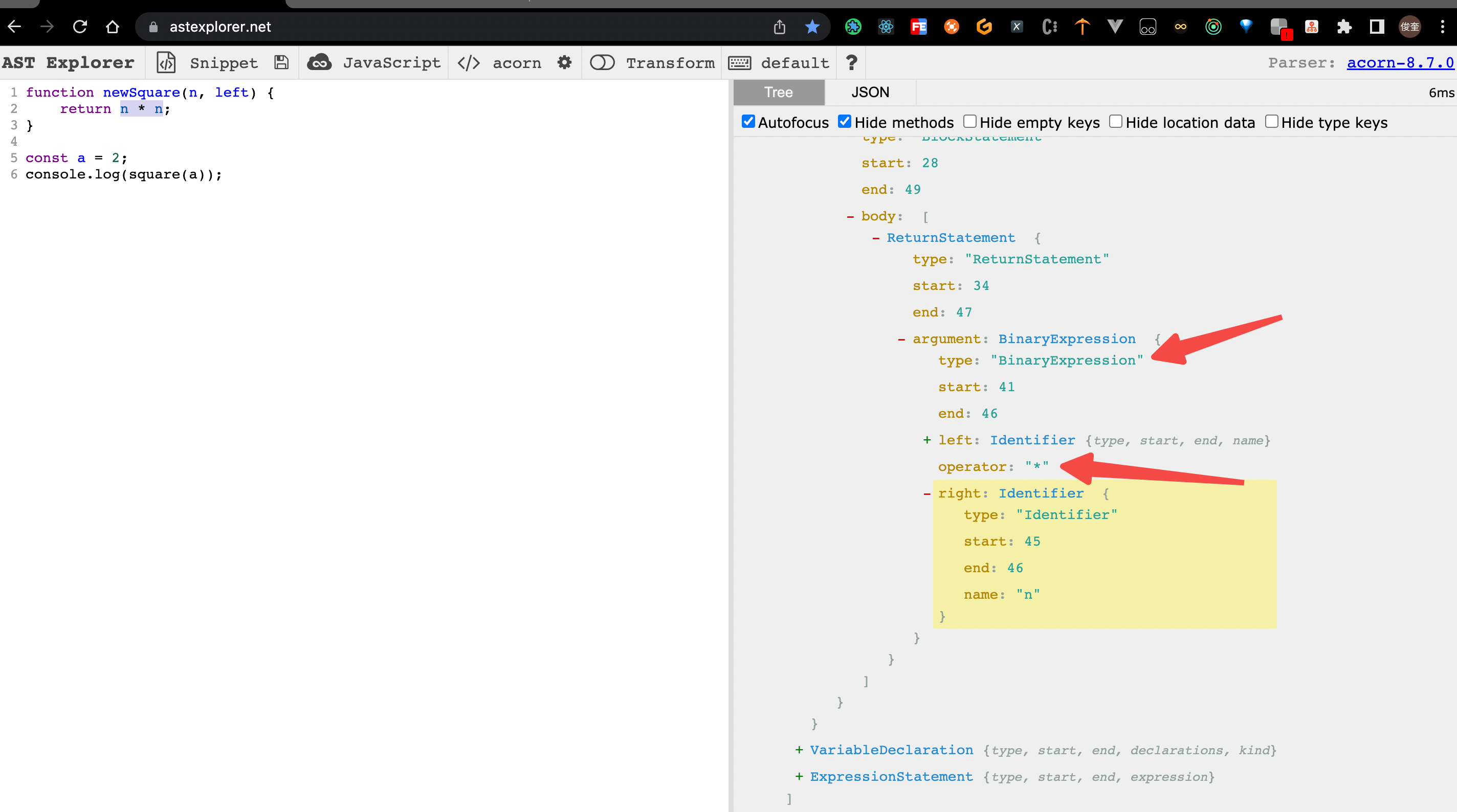
发现 如果单纯的 去 操作 Identifier类型的 n 情况有些多,并且 当前情况 还要 判断 操作符(operator) 是不是
*,换个思路,去操作 BinaryExpression 类型的数据在 BinaryExpression类型 中,仅仅 需要 判断 当前
operator的 属性 是不是 我们需要的*伪代码如下:
BinaryExpression(path, state) {
if (path.node.operator !== "*") return;
console.log("BinaryExpression");
// 替换一个节点
path.replaceWith(
// t.binaryExpression("**", path.node.left, t.NumericLiteral(2))
t.binaryExpression("**", t.identifier("left"), t.identifier("n"))
);
},
6. 最后一步:在调用 square处 进行修改,首先将函数名 改为 newSquare,然后在,对该函数的入参增加 一个 222
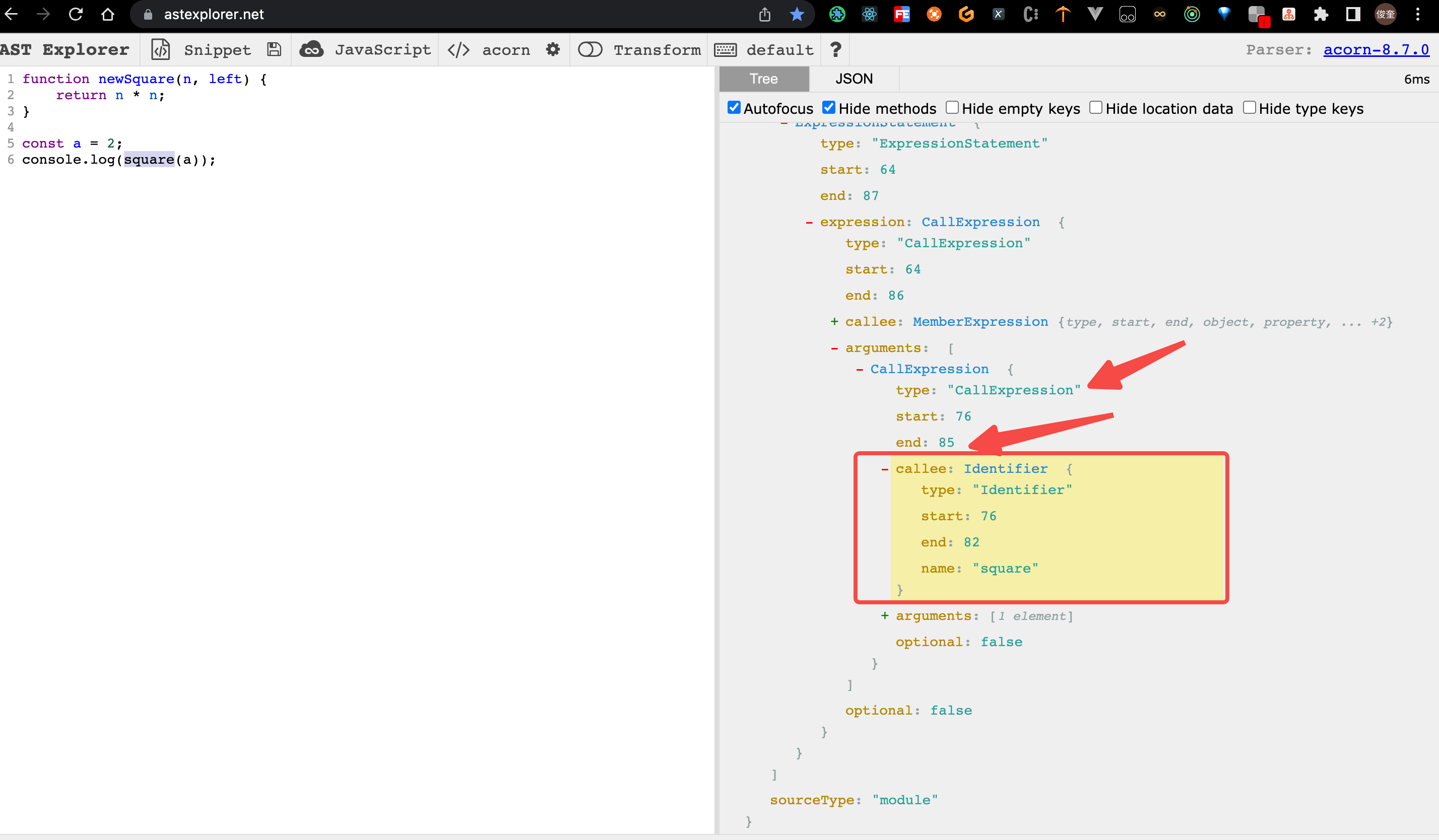
- 目标 是将 name 字段的
square字段 改为newSquare。
方法一:其 父级节点 是一个 CallExpression,直接在其 父级节点 操作 它。
伪代码 如下:
CallExpression(path, state) {
console.log("CallExpression");
// 当前被调用函数的 名称 是 square
if (path.node.callee.name === 'square') {
console.log("在 CallExpression 中,更改 被调用 函数 square 的名字 为", newName);
path.node.callee.name = newName;
}
},
方法二:通过 节点 Identifier 进行操作
- 判断当前 节点的属性是
callee表示是被调用的,并且 当前 节点的 名字 为square
伪代码如下:
// 判断是不是 square 的函数调用
if (path.key === "callee" && path.isIdentifier({ name: "square" })) {
console.log("对square函数调用进行重命名", newName);
path.node.name = newName;
}
7. 总结 以及 全部代码
到现在,你会发现其实 对 ast 语法树的操作,主要还是 操作一个 ast 语法树的对象,只要 对 ast 语法树 对象 进行 符合 ast 语法树 相关规则的 属性的 更改,babel 就会 自动 处理 ast 语法树对象 并生成 新的 代码。
核心代码
// square-plugin.js
// 新建 变量,记录 新函数的函数名
const newName = "newSquare";
module.exports = function ({ types: t }) {
return {
visitor: {
Identifier(path, state) {
console.log("走进 Identifier");
if (path.parentPath && path.listKey === "arguments") {
console.log("增加参数");
path.container.push(t.NumericLiteral(222));
return;
}
// 获取当前 函数的 父级。查找最接近的父函数或程序:
const parentFunc = path.getFunctionParent();
if (parentFunc) {
// 当前父节点 是 square函数 并且当前的节点的listKey是 params(此处是为了排除 square 的函数命名节点)。
// 此处是在重命名后才会走的 逻辑 所以 该节点 父级的 名称判断用的是 newName 而不是 square
if (
parentFunc.type === "FunctionDeclaration" &&
parentFunc.node.id.name === newName &&
path.listKey === "params"
) {
console.log("新增函数参数 left");
path.container.push(t.identifier("left"));
}
// 当前父节点 是 square函数 并且当前的节点的key是 id(此处是为了确认 square 的函数命名节点)。
// 然后对此函数进行重命名 从 square 改为 newName
if (parentFunc.node.id.name === "square" && path.key === "id") {
console.log("对 square 进行重命名:", newName);
path.node.name = newName;
}
}
// 方法二: 判断是不是 square 的函数调用
// if (path.key === 'callee' && path.isIdentifier({name: 'square'})) {
// console.log("对square函数调用进行重命名", newName);
// path.node.name = newName;
// }
},
BinaryExpression(path, state) {
if (path.node.operator !== "*") return;
console.log("BinaryExpression");
// 替换一个节点
path.replaceWith(
// t.binaryExpression("**", path.node.left, t.NumericLiteral(2))
t.binaryExpression("**", t.identifier("left"), t.identifier("n"))
);
},
CallExpression(path, state) {
console.log("CallExpression");
// 方法1: 当前被调用函数的 名称 是 square
if (path.node.callee.name === "square") {
console.log(
"在 CallExpression 中,更改 被调用 函数 square 的名字 为",
newName
);
path.node.callee.name = newName;
}
},
FunctionDeclaration(path, state) {
console.log("FunctionDeclaration");
// const params = path.get('params');
// const params = path.get('params');
// params.push(t.identifier('left'));
// console.log('FunctionDeclaration end', path);
// path.params = params;
// path.params.push(t.identifier('right'));
},
},
};
};